Innovation Through Process Excellence | An Introduction to Lean Six Sigma Applications
Innovation…
happens when a new idea becomes a reality. Be it an individual or a company, one has to have enough passion to overcome the obstacles which is commonly associated with the creativity and innovation process.
“You can’t solve a problem on the same level that it was created. You have to rise above it to the next level.” –Albert Einstein
All over the world, companies and organisations in nearly every industry have seen an increasing need to introduce Lean Six Sigma to increase customer satisfaction and to deliver impressive results especially in these changing and uncertain times.
Advantages of the well-known Lean Six Sigma approach are not so much the tools. Nearly all Lean Six Sigma tools have been around for decades. The advantages of Lean Six Sigma are in having the most talented people in the company – led by the leadership team – working on business-relevant projects whilst getting a very comprehensive training on a structured approach supported by extensive coaching to apply powerful tools…. Uwe H Kaufmann1
We asked Mr. Surajit Dhar, a Lean Six Sigma Applications Facilitator & Coach for Operational Excellence for an introduction and explanation about Lean and Six Sigma.
History of Lean
Lean is a set of tools and techniques. Lean concepts originated with Henry Ford, who introduced production flow in 1913. However, Ford’s techniques were not flexible for new models or colors. Toyota advanced production flow methods in the 1930s to include techniques for handling variations. They reduced costs and increased quality.
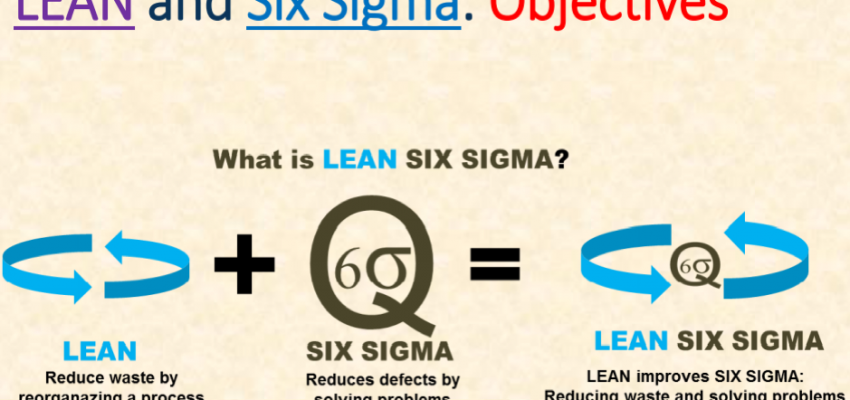
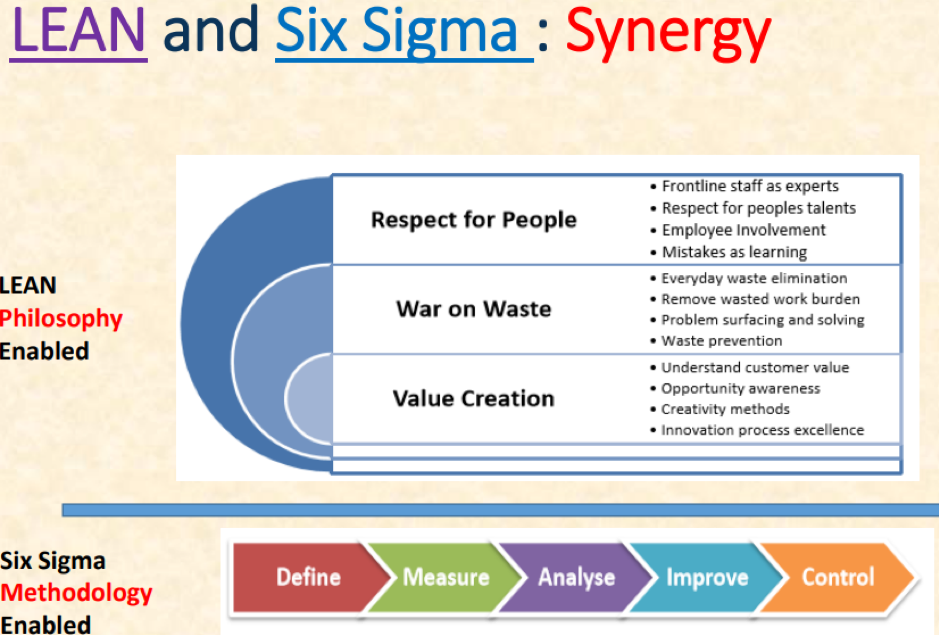
A systematic approach in identifying and eliminating waste (non-value-added activities) through continuous improvement in pursuit of perfection by delivering the product at the pull of the customer.
- Focuses on maximizing process velocity
- Provides concepts & tools for analysing process flow and delay times at each activity in a process
- Centres on the separation of “value-added” from “non-value added” work with tools to eliminate the root causes of non-value add activities and their cost
- Provides a means for quantifying and eliminating the cost of complexity

History of Six Sigma
Six Sigma (6σ) is a set of techniques and tools for process improvement. It was introduced at Motorola in 1986 and at General Electric in 1995. A six sigma process is one in which products delivered are statistically expected to be free of defects.
Six Sigma strategies seek to improve the quality of the output of a process by identifying and removing the causes of defects and minimizing impact variability in manufacturing and business processes. Each Six Sigma project carried out within an organization uses a set of quality management methods and follows a defined sequence of steps and has specific value targets, for example: reduce process cycle time, reduce pollution, reduce costs, increase customer satisfaction, and increase profits.
- Emphasizes the need to recognize opportunities and eliminate defects as defined by customers
- Recognizes that variation hinders our ability to reliably deliver high-quality services
- Requires data-driven decisions and incorporates a comprehensive set of quality tools under a powerful framework for effective problem solving
Watch this short clip where Mr. Surajit Dhar explains how Lean Six Sigma can be applied in any industry in this video.
Reference:
- Lean Six Sigma and Innovation by Uwe H Kaufmann https://coe-partners.com/innovation-six-sigma/

0 Comments